Plastic is usually made from dead dinosaurs (read fossils). They turn into crude oil, the oil turns into petrol, and we turn the petroleum into plastic.
However, what if I told you that we can make plastic that is biodegradable, from plants? Sounds far-fetched, but I promise you that it is true.
Table of contents:
- What are the problems with regular plastic?
- What are bioplastics?
- How are hemp bioplastics made?
- The pros and cons of hemp bioplastics
- The future of hemp as a bioplastic
You’ve heard about the benefits that hemp textiles will bring to the fashion industry. This article is about the benefits that hemp brings to another industry — plastics.
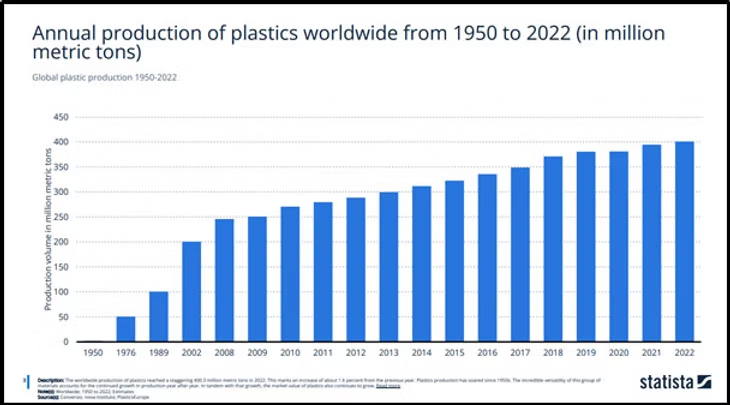
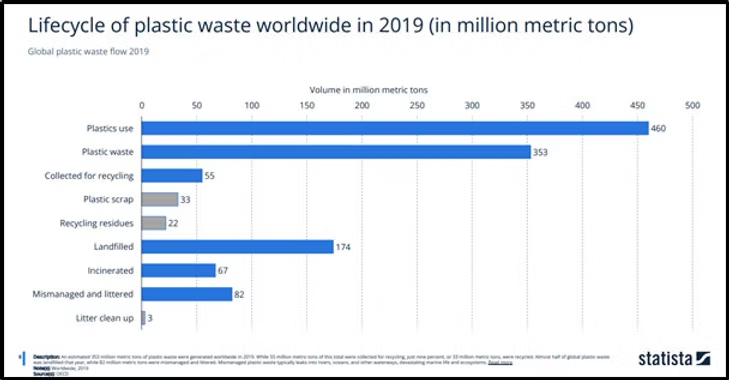
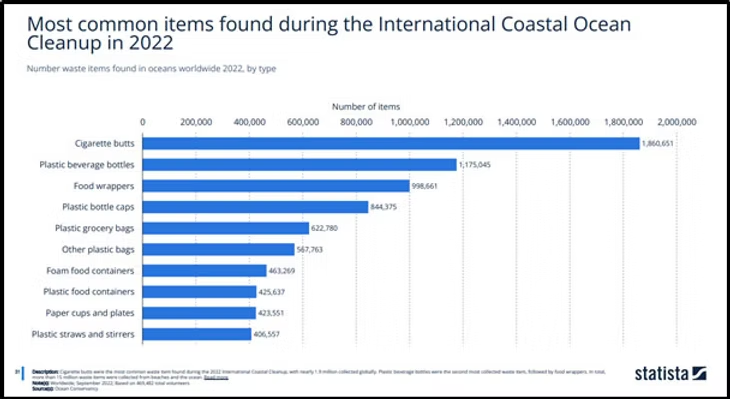
Plastic accounts for 10% of the world’s carbon and 65% of it ends up in the ocean. And the production is only going up.
Here’s how hemp bioplastics can solve (some) of our plastic problems.
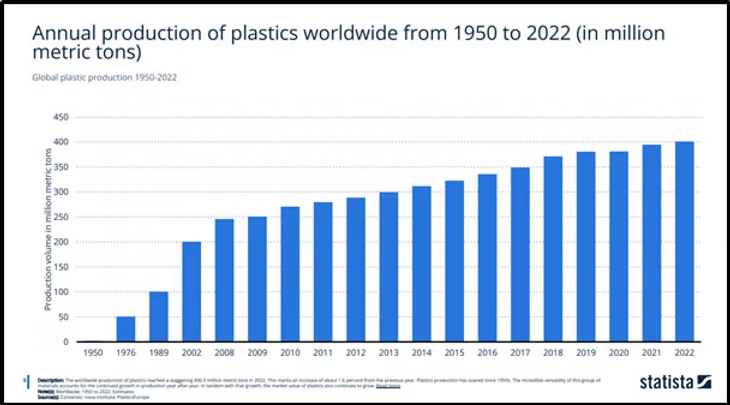
Table of contents:
- What are the problems with regular plastic?
- What are bioplastics?
- How are hemp bioplastics made?
- The pros and cons of hemp bioplastics
- The future of hemp as a bioplastic
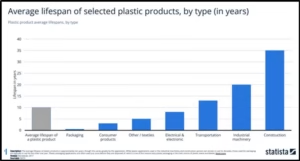
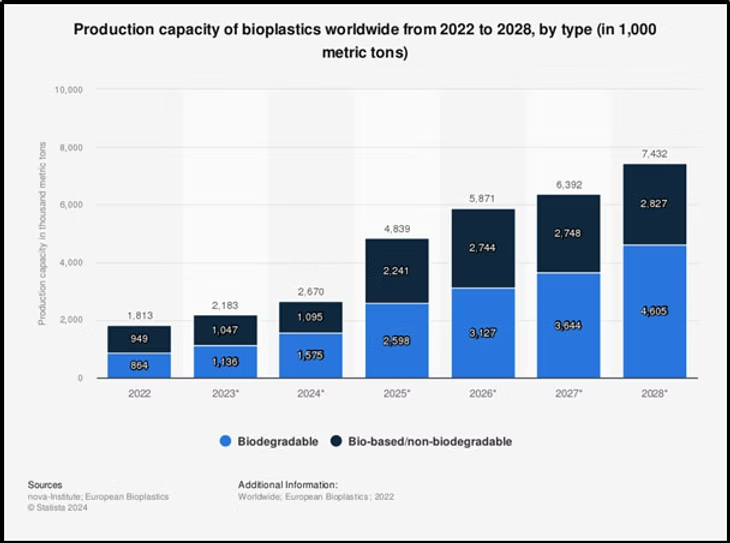
What are bioplastics?
- First, the outer bast fibers are removed from the hemp stem or stalk. This is through a process called decortication. This leaves behind the inner woody core known as a hurd.
- Next, this hurd goes through processing to extract the cellulose from the plant. S3EJHSAHWAYSYYTHEEZHSBthAMNĒṬZ–XKIFIVarious methods like chemical treatment or enzyme treatment can be used.
- The extracted cellulose is then transformed into plastic polymers. This step is called biosynthesis or synthetic conversion. Biosynthesis uses bacteria or other microbes, while synthetic routes rely on chemicals.
- The result? You get a bioplastic polymer resin that can be molded, extruded or processed. And it is just like conventional plastics, and can be turned into a huge variety of products.
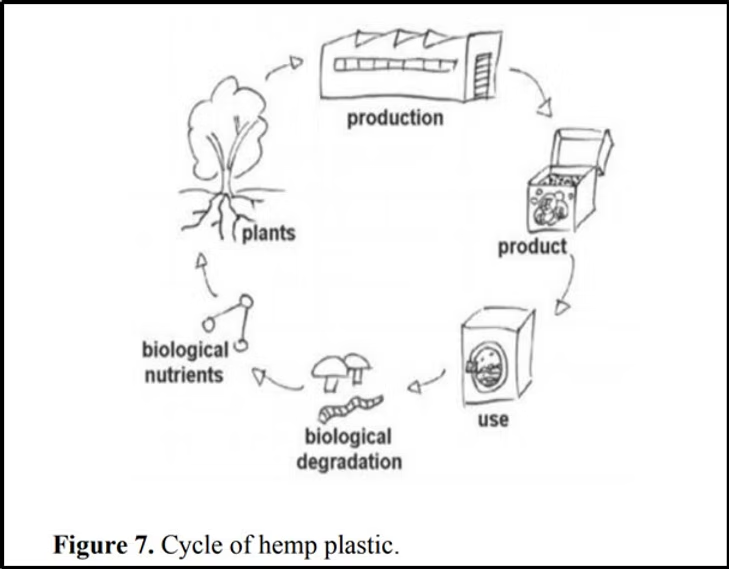
Plus, hemp is incredibly renewable.
It can be harvested and replanted in the same soil every 4 months without depleting the land. Contrast that to annual crops that need rotation.
-
High Strength and Durability
-
Lower Environmental Impact
-
Fully Biodegradable
-
Affordable and Scalable
-
Versatile Applications
-
Limited Supply Chain
-
Technical Limitations
-
Unclear Regulations
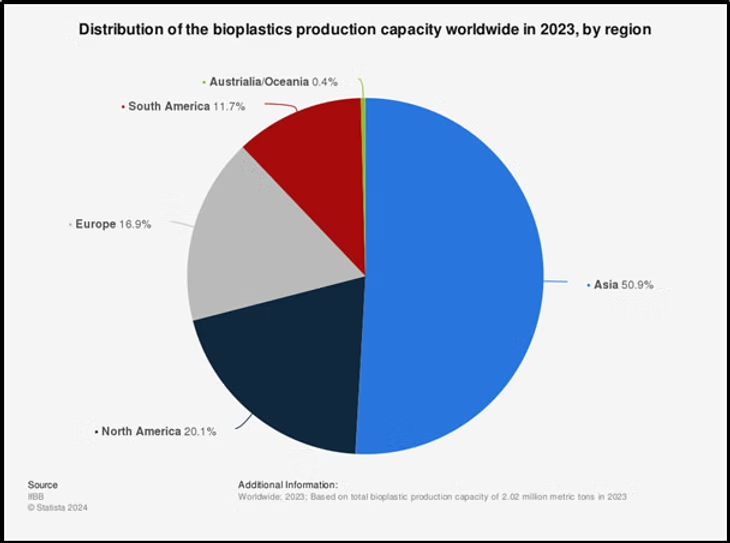
Why is hemp so well-positioned?
For one, it requires far less water than traditional bioplastic crops like corn. One estimate finds hemp needs only 1/20th the water versus cotton [from the North American Industrial Hemp Council].
Hemp is also remarkably fast-growing. It can be harvested and replanted on the same land in just 4 months, allowing multiple crops per year. Contrast that to annually replanted crops like corn.
Perhaps most importantly, hemp cultivation has a strongly negative carbon footprint.
Hemp bioplastics are the ideal solution for meeting emission and pollution reduction targets. Given that hemp grows so quickly, and can be planted multiple times a year, it is a great feedstock for bio plastics.
The biggest hurdle right now is establishing efficient supply chains. When that is taken care of, the only happy problem we will have is keeping up with demand.
______________________________________________________________________________
- https://hempfoundation.net/hemp-bioplastics-current-market-and-future/
- https://www-statista-com.ezproxy.mdx.ac.uk/study/65164/plastic-waste-worldwide/
- https://www-statista-com.ezproxy.mdx.ac.uk/statistics/678684/global-production-capacity-of-bioplastics-by-type/
- https://www-statista-com.ezproxy.mdx.ac.uk/statistics/678811/production-capacity-distribution-of-bioplastics-worldwide-by-region/
- https://europlas.com.vn/en-US/blog-1/the-pros-and-cons-of-hemp-bioplastic
- https://hempplastic.com/
- https://www.packaging-gateway.com/features/is-there-potential-in-hemp-for-bioplastics/?cf-view
- https://hempfoundation.net/hemp-plastic/
- https://sanapackaging.com/blogs/news/understanding-hemp-plastics
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327203397_Hemp_is_the_Future_of_Plastics